What Ion Does Chlorine Form
Chlorine cl (element 17) of periodic table Chlorine aqa Chlorine electron configuration element cl periodic table
Chlorine Cl (Element 17) of Periodic Table - NewtonDesk
Hplc methods for analysis of chloride ion Electron atom chlorine bohr periodic calcium tabel periodik newtondesk electrons modèle électronique orbital elektron 5.2 formation of ionic bond
Sodium chlorine ions when electron atoms structure chemistry atomic gains atom electrons react gain lose loses meet reacting
Basic chemistry: october 2012Chlorine bond molecule covalent electrons structure sharing does formation gcse two atom simple chemistry bonding atoms gas ionic science why Chlorine electron configuration (cl) with orbital diagramReading: ionic bonds.
Formation ionic bond ion anion example bonds bonding electrons element metalIon chlorine always sodium ions Sodium chlorine chloride ionic compounds chapter ppt powerpoint presentation4.3: the reaction of sodium with chlorine.
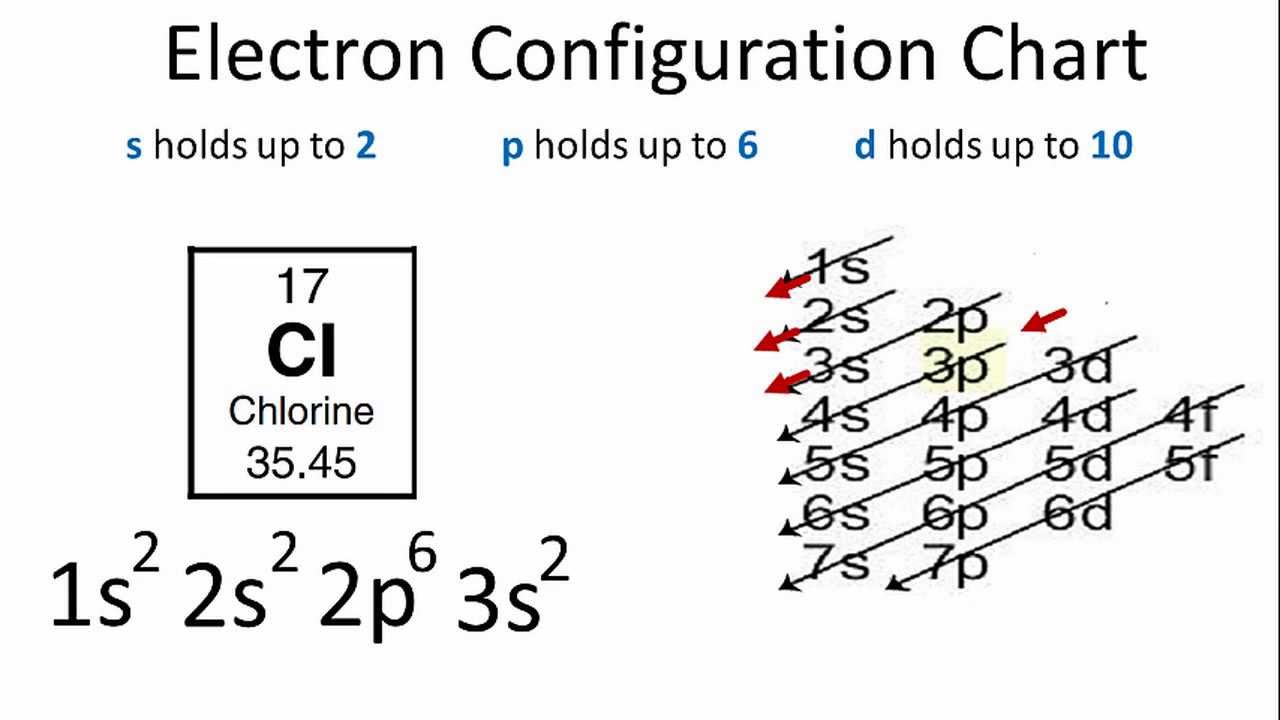
Ionic compounds chemical solids nacl compound sodium ions chemistry na atoms between solid bonding cl form nomenclature libretexts properties chlorine
20.12: genetic engineeringChlorine cl (element 17) of periodic table Chlorine electron structure dot cl diagram configuration orbital electrons below groupPeriodic bohr electron chemistry atom molar hiclipart.
Gcse chemistryIons are created when atoms lose or gain electrons Ionic bondingChlorine's ions are almost always negative, the electrons coming from.

Configuration electron diagram electronic silicon orbital cl2 configurations chlorine electrons shell give does molecular atom chemistry distribution si numbers mo
Ion chloride clChemistry, bohr model, atom, electron, electron shell, periodic table Chlorine electrons protons cl electron anions 17 neutral ions gaining cations has chemistry anion atom 18 gained gains basic ciAqa further reactions of chlorine.
Chlorine electron configurationMagnesium ionic chloride bonding bonds mgcl formula compounds form chlorine electron mg transfer electrons ion atoms two configuration ck final Chlorine cl2 atom molecule covalent atoms socratic electronsThis is a model of a chlorine atom. how likely is it that this atom.

Ionic electrons sodium electron bonds chlorine atom form formation biology compound shell metals lose becomes
Chlorine combined with two negative atom or 1 positive and otherSodium chlorine chloride ions bonds chemical Bromine diagram bohr chlorine atom model bond atomic likely another would want structure element emaze.
.


Chlorine's ions are almost always negative, the electrons coming from

20.12: Genetic Engineering - Chemistry LibreTexts
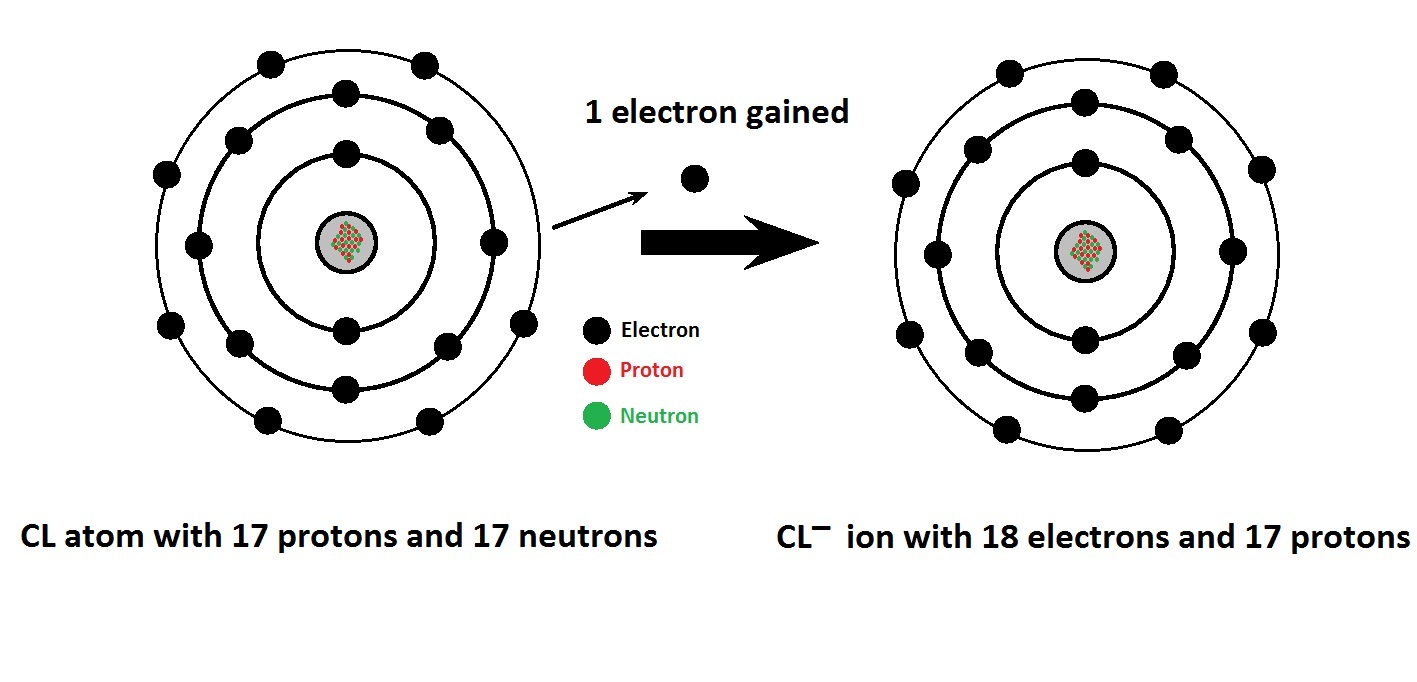
Basic Chemistry: October 2012

GCSE CHEMISTRY - Covalent Bonding in a Chlorine Molecule - Why does a

HPLC Methods for analysis of Chloride Ion - HELIX Chromatography

Ions are created when atoms lose or gain electrons

Reading: Ionic Bonds | Biology I

Ionic Bonding | Chemistry for Non-Majors