Derived Characteristics Of Humans
Ancestral derived vs cladogram basic constructing activity studylib Derived ancestral slidesharetrick 2. primate classification – the history of our tribe: hominini
PPT - Chapter 4: Speciation and Phylogeny PowerPoint Presentation, free
What is a derived character 6th winmeen Humans human characteristics presentation bipedal locomotion brain large
Taxonomy derived organisms characteristics cladograms biologyjunction
What is a derived characterHuman evolution notes 6th social science Cladogram primate primates classification clade cladograms evolutionary tree phylogenetic evolution monkey ancestor taxonomic common lorises cladistics ape lemurs orangutan chimpanzeeDerived cladograms slidesharetrick.
Derived clade cladogram slidesharetrick clades descent driverlayerSpeciation phylogeny chapter ancestral trait derived traits common ancestor tree similarity analogous using Derived characters taxonomy ppt powerpoint presentationEukaryotes and their origins.

Eukaryotes origins evolutionary gatech biosci
Evolution: synapomorphies & cladogramSynapomorphy between difference cladogram synapomorphies evolution shared traits phylogeny derived ancestral trait character homoplasy which terminology vs tree definition examples Basic cladogramDerived character biological characteristic diversity origins ch organisms ppt powerpoint presentation evolves unites clade lineage arises over time.
Solved consider the cladogram with shared and derivedDerived cladogram ancestral ancestor primitive primates humans gorillas consider labeled evolutionary Phylogenetic biology evolutionary cladistics relationships tree clade clades life trees fungi plants shared organisms animals characteristics species different history groupsDerived classification evolutionary.


PPT - Ch. 15: Origins of Biological Diversity PowerPoint Presentation
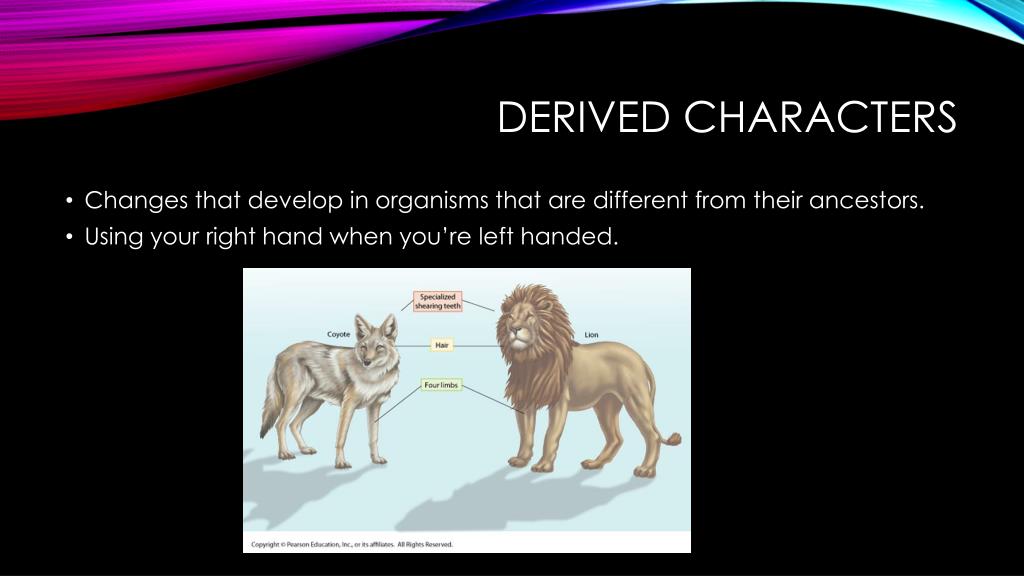
PPT - Taxonomy PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:3021263
What Is A Derived Character - slidesharetrick

Human Evolution Notes 6th Social Science - WINMEEN

Evolution: Synapomorphies & Cladogram | SchoolWorkHelper

Taxonomy - BIOLOGY JUNCTION

Solved Consider the cladogram with shared and derived | Chegg.com

PPT - Humans PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4116646

Basic Cladogram

Cladistics | Biology for Non-Majors II